- What is Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A)?
- What are FP&A Tools?
- Key Features of FP&A Tools
- Common FP&A Tools
- Cube
- Anaplan
- Workday Adaptive Planning
- Vena
- Prophix
- Oracle Hyperion
- NetSuite Planning and Budgeting
- Datarails
- The Role of FP&A Tools in Corporate Finance
- Considerations for Choosing FP&A Tools
- Best Practices for Choosing and Implementing FP&A Tools
The Best FP&A Tools: Key Considerations and Popular Tools for Any Organization
What is Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A)?
Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A) teams play crucial roles by performing budgeting, forecasting, and analysis to support informed decision-making.
As part of this, FP&A requires extensive data reconciliation and consolidation, as well as understanding and interpreting variance analysis. Additionally, FP&A professionals perform different scenario and sensitivity analyses to forecast possible outcomes.
In other words, FP&A connects the accounting team to the management team by analyzing data and presenting findings and recommendations to upper management and other decision-makers. As such, FP&A is heavily involved in developing and maintaining company strategy.

Key Highlights
- Traditionally, FP&A teams primarily used Microsoft Excel for data analysis, financial analysis, and strategic planning. However, Excel has some limitations and inefficiencies, especially as companies grow in size and complexity.
- Because of these limitations, software companies created purpose-built FP&A tools. These tools are designed to allow for better collaboration and speed, as well as improve data connectivity and reduce error-prone, manual work.
- Key features of FP&A tools include better data management, visualizations, scenario analysis, and automation, among other features. There are also many considerations a team must factor when choosing and implementing software.
What are FP&A Tools?
Microsoft Excel
Traditionally, finance teams primarily used Microsoft Excel to compile data, analyze key performance indicators (KPIs), and create budgets and forecasts. However, while Excel is still widely used in FP&A, it has some limitations, especially as companies grow in size and complexity.
Some of the issues with relying on Excel in FP&A are:
- Although widely used and fairly easy to understand, Excel often requires significant manual data entries, reducing efficiency and increasing the likelihood of errors.
- Excel is mostly ideal for a single user or a small number of users. If significant collaboration is necessary, then sharing an Excel file can lead to multiple different challenges:
- Users creating multiple versions of a file, resulting in the lack of a “single source of truth.”
- Difficulty establishing audit trails and determining what may have changed in the collaboration process.
- Additionally, it’s often difficult to create an Excel file that allows users to make quick changes and communicate those changes in a coherent way for decision-makers. This is crucial in a dynamic and fluid business environment.
Because of these issues, many companies have created specialized software tools to reduce or eliminate these drawbacks of using Excel.
Beyond Excel: Benefits of FP&A Tools
FP&A software tools are designed to reduce the reliance on Excel and its limitations. FP&A software helps:
- Optimize collection and consolidation of financial (and non-financial) data.
- Enable collaborative and integrated business planning, forecasting, and budgeting.
- Ability to quickly run different scenarios and what-if analysis.
- Dynamically present results using compelling data visualization tools.
- Use real-time analytics for up-to-the-minute monitoring of important KPIs.
- Keep data safe and secure.
Because of this, many software companies decided to create purpose-built FP&A tools for situations in which Excel was not particularly well-suited. These tools are designed to allow for better collaboration and speed, as well as improve data connectivity and reduce manual work.
Key Features of FP&A Tools
FP&A tools are designed to improve upon using Excel spreadsheets across an entire business. With that in mind, some of the key features of analysis software include:
- Data Management: As businesses grow, the amount of generated data will grow at the same rate, if not faster. Managing this data — and converting it into something actionable — is not something Excel was designed to handle easily. Having a centralized and reliable data source is necessary so that business leaders in different roles can all see the same data, helping lead to improved financial performance and obtaining key business objectives.
- Data Visualization: While Excel is definitely capable of creating nice visuals and charts, it’s often difficult for even experienced users to get these visualizations created in the best (and most efficient) manner. Ideally, planning software will include easy-to-use and robust visuals so that the most important and impactful data is communicated to business leaders.
- Data Integration: FP&A software will need to be able to integrate with existing platforms and data sources, including Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software, among other potential data sources.
- Scenario Analysis: Scenario and sensitivity analysis is a necessary function for any FP&A tool. Finance professionals need the ability to see the outcome of a variety of situations to properly consider an action. This helps prepare organizations for uncertain futures by enabling a better understanding of potential outcomes.
- Collaboration Ability: FP&A is a highly collaborative role, and the finance team will need to work with other departments and functions. Therefore, any software solution should have strong collaborative features like shared dashboards and comment sections. These features enable different teams to effectively work together.
- Data Security: FP&A software should include features to ensure data security and compliance with the appropriate regulations and standards. Data security features will usually include audit trails, different levels of access, as well as data encryption.
- Real-time Analytics: An ideal feature would also be access to real-time analytics. This enables organizations to monitor the financial health of the company in real time, which could lead to making quick business decisions if necessary.
- Tasks Automation: A lot of FP&A work involves manual data entry and cleaning data so that it can be analyzed. A good software solution should have the ability to reduce this time-consuming and error-prone work via automation.
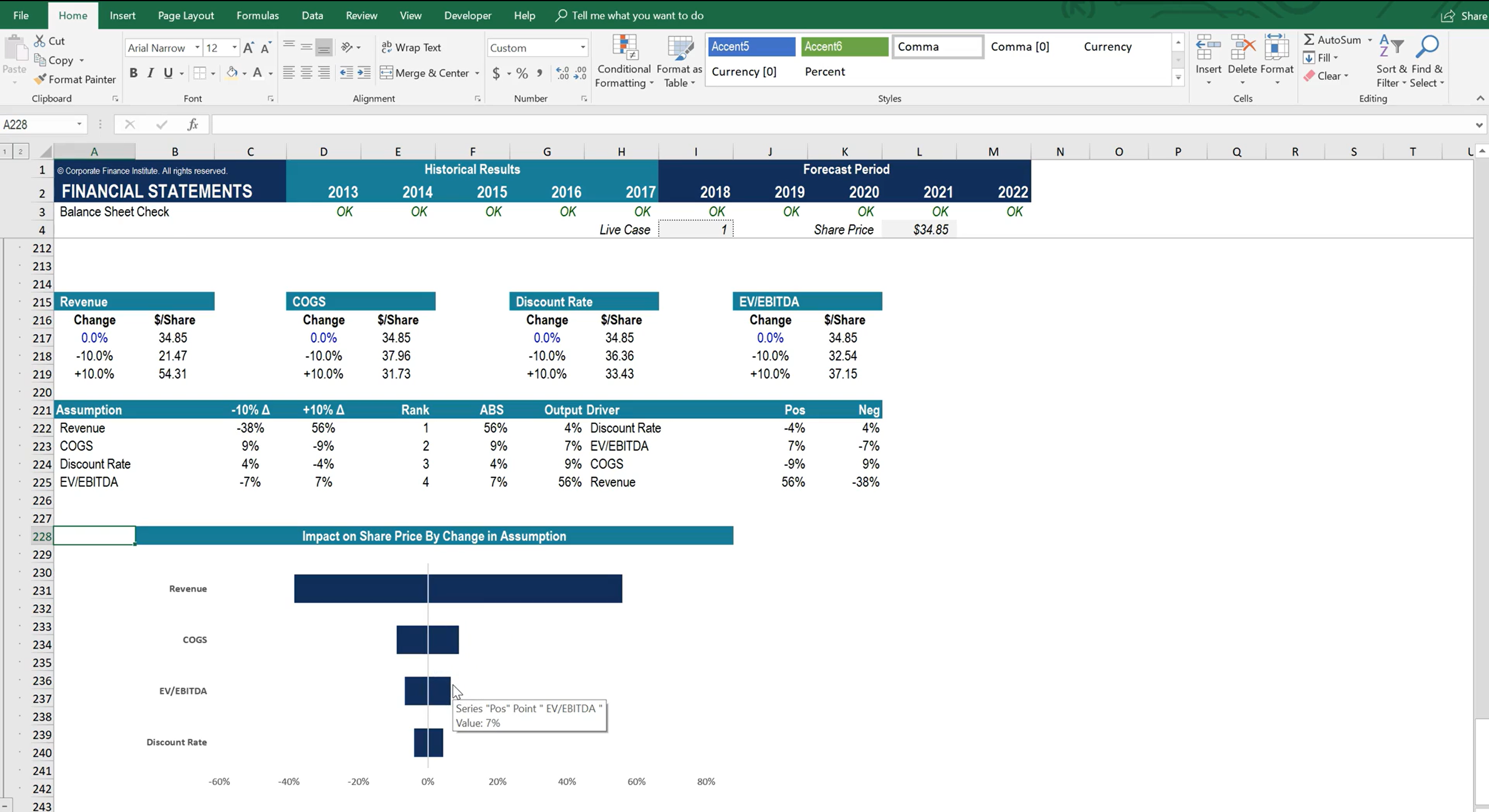
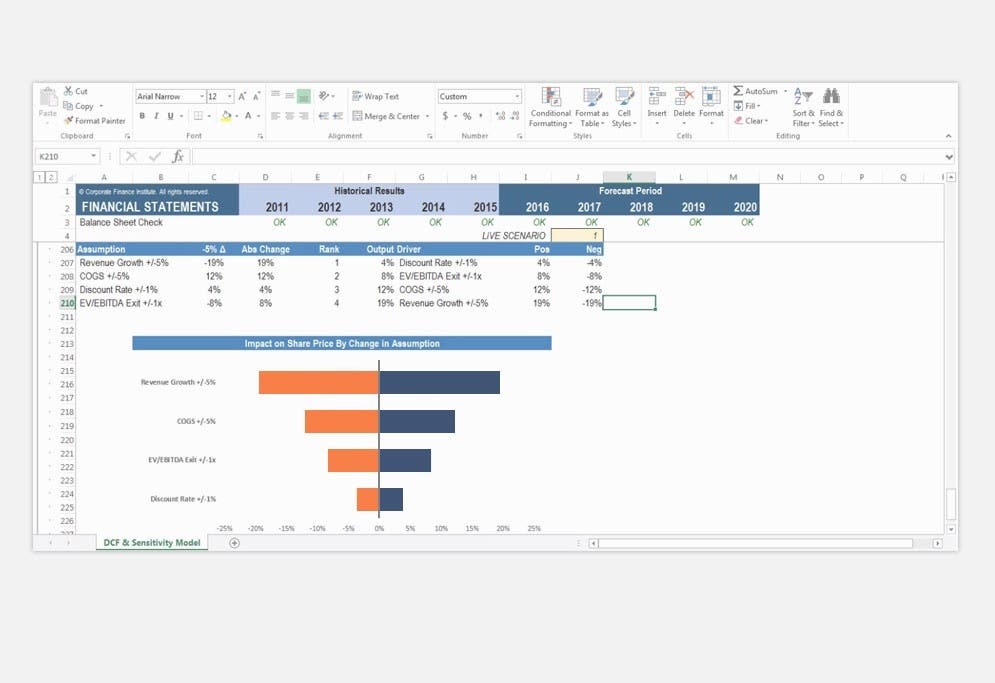
Image from CFI’s Scenario & Sensitivity Analysis in Excel course
Common FP&A Tools
FP&A tools are built by a range of companies, including relatively small software companies to some of the largest technology-focused companies in the world. Some of the most commonly used tools are better for small and medium-sized businesses, and some are better for large companies.
The following are some of the most common and well-regarded tools for FP&A professionals (in no particular order).
Cube
Cube is a spreadsheet-native FP&A tool, making it user-friendly and able to be easily added to existing workflow and processes. Cube reduces the amount of manual work and allows for better control compared to spreadsheets.
Anaplan
Anaplan is a large, enterprise-wide solution that allows users to model complex business scenarios and connect the outcomes to the overall company strategy. This FP&A software is best suited for larger companies with deeper project management experience and more information technology (IT) resources. In addition to financial planning and analysis, Anaplan can also be used for operational planning processes and cost management practices.
Workday Adaptive Planning
Workday Adaptive Planning is a “one-stop shop” for all of a company’s planning needs. This tool covers financial planning, including budgeting and forecasting, as well as analytics and reporting. It can also help with workforce and headcount planning, sales planning, and marketing planning. This wide range of features allows for collaboration across an entire company. Workday Adaptive Planning is best for large companies seeking a solution that is not just focused on finance and FP&A.
Vena
Like Cube, Vena also incorporates Excel as part of its FP&A tool. Vena offers pre-built templates to automate tasks, but the user can also create their own customized workflows and templates. Additionally, Vena offers enterprise-level security and more in a structured database environment. Vena is most useful for companies that have yet to develop strong FP&A practices and that currently require some guidance.
Prophix
Prophix uses a single platform to help FP&A teams automate repetitive tasks. This single-platform model helps ensure there is one source of truth to the numbers and allows for better collaboration across functions and teams. Prophix is suited for companies with a lot of manual and repeatable tasks and processes.
Oracle Hyperion
Hyperion is a centralized planning, budgeting, and forecasting tool that can incorporate both financial and operational processes to improve the efficiency and capability of FP&A teams. Hyperion is typically used by large organizations that already use a suite of Oracle products and solutions.
NetSuite Planning and Budgeting
NetSuite’s planning and budgeting feature can connect to different enterprise solutions to streamline and improve both company-wide and departmental budgeting and financial planning. This tool is better for medium or large enterprises since it has features and tools that might not be as useful for smaller businesses.
Datarails
Datarails is a popular FP&A software for small and medium-sized businesses. Like some of the other tools, Datarails directly incorporates Excel into the FP&A tool, increasing adaptability and ease of use.
In addition, there are many other great FP&A tools not mentioned above, including Planful, Jedox, and OneStream, among others.
The Role of FP&A Tools in Corporate Finance
FP&A software is a somewhat generic term for many different systems that help monitor a company’s financial health as well as better inform its strategic decision-making.
In general, financial planning software includes the following different processes and responsibilities:
- Budgeting and Forecasting Tools: Budgeting and forecasting tools help companies better prepare detailed budgets and forecasts. This software enables better collaboration compared to Excel and maintains version control so that there is only a source of truth that users can see. Budgeting and forecasting allow companies to set and monitor targets, which allows decision-makers to tactically pivot certain strategies as necessary. These tools also allow scenario planning to support decisions in a dynamic, fast-paced environment.
- Financial Reporting Tools: Financial reporting tools are a little different from budgeting and forecasting, but they are still used by FP&A teams when preparing analyses and actionable insights for management. Financial reporting tools help prepare the three key financial statements, which allows for statutory reporting as well as the ability to prepare more-specific, tailored reporting for management.
- Performance Management Tools: This type of tool is important for corporate performance management. Performance management is a broad category that allows key stakeholders the ability to monitor both financial and operational data. Being able to monitor this data in real time allows a company to remain agile when business conditions change.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Tools: BI software overlaps with FP&A in that BI tools provide advanced data analytics as well as robust visualization tools designed to quickly and easily communicate analyses and courses of action.
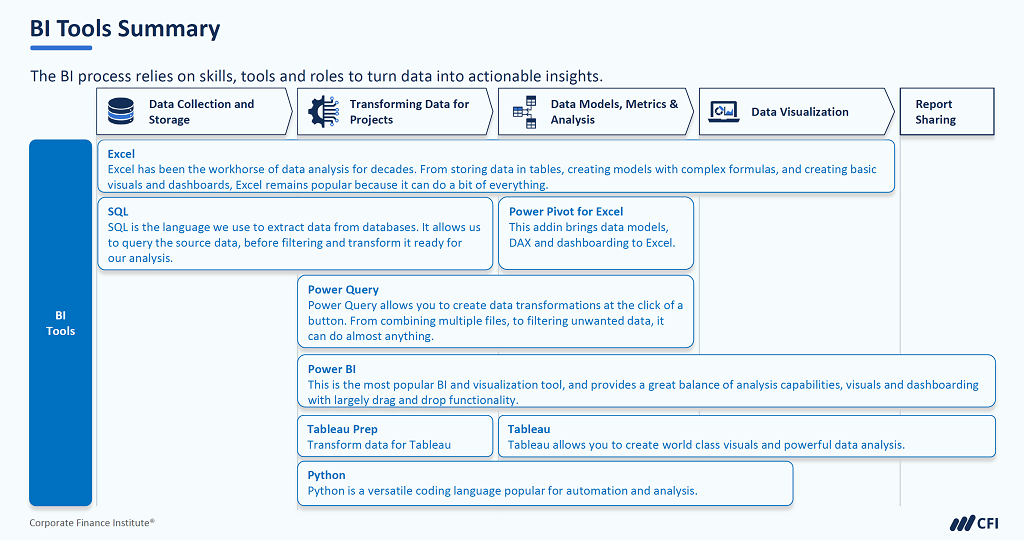
Image from CFI’s Introduction to Business Intelligence course
Considerations for Choosing FP&A Tools
There are many factors to consider when determining which FP&A tool is right for your organization.
- Ease of use: Any FP&A software solution must be relatively easy for users to ensure sufficient buy-in and adoption. Ease of use will also help increase productivity, which is ultimately the main goal of using these tools.
- Integration with existing systems: Most companies already have existing software or systems to help run the business. It’s absolutely critical that any FP&A tool has the ability to seamlessly integrate with these existing systems. If not, then the investment in an FP&A tool could be wasted or the company will also have to adopt costly new systems.
- Size and resources: When deciding on the proper tool, company size and sophistication play an important role. Larger companies tend to have more resources and can more easily dedicate these resources to implementing and maintaining new tools. Smaller companies may not have this ability and may benefit from tools that already have pre-existing templates.
- Scalability: Any consideration must also consider if the solution is scalable. As a company grows, its needs will grow as well. Choosing the proper software solution must weigh how easily the software can accommodate growth without compromising performance.
- Customization: While many companies can benefit from pre-built templates, it’s also important for clients to be able to create customized solutions. Customizing FP&A tools may be necessary to better align with a company’s existing processes as well as increase user adoption, thereby boosting efficiency.
- Budget: The cost of any FP&A solution will always be a factor in choice. The most obvious cost is likely the initial purchase of the tool or ongoing licensing fees. But any decision also needs to consider the total cost of ownership, which could include implementation and training costs, as well as maintenance and support costs, among others. Failure to consider all costs will directly impact the tool’s return on investment (ROI).
- Existing FP&A processes and capabilities: If a company already has a highly experienced FP&A team, then it may not need tools that come with pre-built templates or processes. Instead, the company may opt for a more technically intensive tool since the team can leverage existing knowledge to design or create its own workflow, automation, and visualizations.
- Cloud-based tools versus on-premises tools: FP&A software may be cloud-based or on a company’s premises, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages. Cloud-based tools allow for greater accessibility, which is crucial in work-from-home or hybrid jobs. All a user needs is an internet connection. However, storing sensitive data in the cloud could create issues around data breaches and unauthorized access. On-premises tools may allow for greater security and more control but are typically more expensive with a large initial investment and ongoing maintenance and upkeep.
- Customer support and training: No matter how easy the FP&A software is to use, there will always be the need for good customer support to help troubleshoot and fix any issues that arise. Additionally, initial training on the tool not only helps adoption but can enable users to proactively find solutions before relying on customer support.
- Data security: Finance teams are exposed to highly sensitive financial and operational data. Therefore, it’s absolutely critical that any FP&A tool has excellent data security to help prevent unauthorized access and potential loss of control. Proper data security helps an organization maintain trust and credibility and may, in fact, be a regulatory or legal requirement.
Best Practices for Choosing and Implementing FP&A Tools
To ensure proper implementation of any financial planning software, an organization should consider some of the following best practices.
- Needs assessment: Teams should always start with a clear understanding of what they need from any software tool. Questions that should be asked and answered are things like “What problems are we trying to solve?” and “How will the software solution integrate with existing systems?”.
- Involve key stakeholders: All potential stakeholders should be involved in the software decision, not just members of the finance teams. The choice and implementation of any software requires resources, including IT professionals, project management, and end users. Securing the input of all affected parties is crucial for ensuring the solution meets the needs of the organization.
- Training and support: When choosing and implementing software, there will always need to be training, not just for end users but also for IT support staff. How much training is necessary and how will it be conducted (synchronous or asynchronous). Additionally, software solutions will always require some level of continuing support from the various software vendors, so it’s necessary to consider that as well.
- Continuously evaluate: To ensure the software is working well, an organization needs to continuously evaluate it. In order to do this, the organization needs to define what success looks like, including deciding on proper metrics and outcomes. These metrics and outcomes need to be clearly defined in order to objectively measure the tool. As part of the evaluation process, it’s also important to regularly review the tool and the metrics, gather feedback from stakeholders, and analyze the return on investment. Both direct financial gains and indirect benefits (better efficiency and improved customer satisfaction) need to be considered when analyzing ROI.
Additional Resources
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide on FP&A Tools. To keep advancing your career and skills, the following CFI resources will be useful:
Additional Resources
CFI is a global provider of financial modeling courses and of the FMVA Certification. CFI’s mission is to help all professionals improve their technical skills. If you are a student or looking for a career change, the CFI website has many free resources to help you jumpstart your Career in Finance. If you are seeking to improve your technical skills, check out some of our most popular courses. Below are some additional resources for you to further explore:
The Financial Modeling Certification
Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in