- Understanding Market Risk
- What is Market Risk?
- How Market Risk Can Impact Financial Institutions' Performance
- Types of Market Risk
- Identifying and Measuring Market Risk
- Managing Market Risk
- Diversification
- Hedging
- Stress Testing and Scenario Analysis
- Liquidity Management
- Constant Monitoring and Rebalancing
- Volatility Management
- Quantitative Analysis and Models
- Regulatory Compliance
- The Role of Risk Management Professionals
- Conclusion
Market Risk Fundamentals
Fluctuations in the prices of financial instruments can lead to unexpected losses
Understanding Market Risk
Understanding market risk is crucial for financial professionals, investors, and anyone involved in the financial markets. Market risk, also known as systematic risk, can impact financial performance significantly, and effectively managing it is essential for achieving long-term financial stability and growth.
This article explores various aspects of market risk, how it affects financial institutions, and the strategies for identifying, measuring, and managing it.
What is Market Risk?
Market risk refers to the potential financial losses that arise from fluctuations in the prices of financial instruments due to changes in market conditions. These fluctuations can result from various factors, including changes in interest rates, stock prices, commodity prices, and foreign exchange rates. Unlike specific risks that affect individual securities, market risk affects the entire market, making it unavoidable but manageable through a robust risk management strategy.
How Market Risk Can Impact Financial Institutions’ Performance
Financial institutions, such as banks, investment firms, and insurance companies, are particularly vulnerable to market risk. Fluctuations in interest rates, stock market volatility, and changes in foreign exchange rates can lead to significant financial losses. For example, if interest rates rise, the value of fixed income securities held by a bank might decrease, leading to lower profits. Similarly, a sudden drop in stock prices can affect investment portfolios, reducing the market value of assets and impacting the institution’s overall financial health.
Key Highlights
- Market risk refers to the potential financial losses that arise from fluctuations in the prices of financial instruments due to changes in market conditions.
- Different types of market risks include interest rate risk, commodity price risk, and exchange rate risk, among others.
- Effective market risk management involves a combination of strategies to mitigate potential losses and protect financial performance.
Types of Market Risk
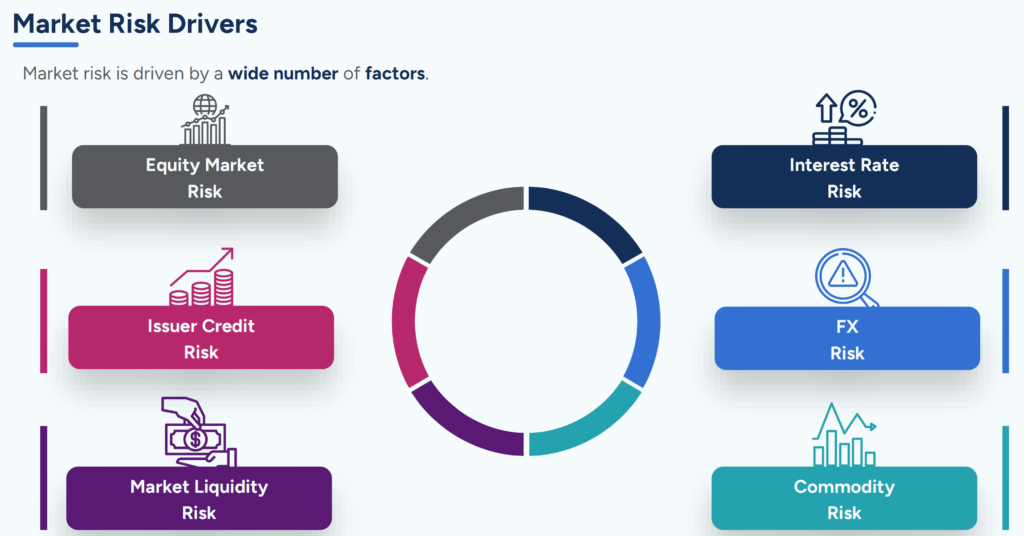
Understanding the different types of market risk is essential for effective risk management. The most common types of market risk include:
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk arises from changes in interest rates that can affect the value of fixed income securities, loans, and deposits. When interest rates rise, the market value of existing bonds typically falls, leading to potential losses for bondholders. Conversely, when interest rates decline, bond prices increase.
Equity Risk
Equity risk is the risk of loss due to changes in stock prices. Equity risk affects both individual stocks and broader market indices. The equity risk premium is closely associated with equity risk. This premium is the excess return that investors require for investing in equities over risk-free assets, such as government bonds.
Commodity Risk
Commodity risk is the potential financial losses resulting from changes in commodity prices, such as oil, gold, and agricultural products. Commodity prices can be highly volatile, influenced by geopolitical events, supply and demand dynamics, and market speculation.
Currency Risk
Currency risk, or exchange rate risk, arises from fluctuations in foreign exchange rates. Companies engaged in international trade or holding investments in foreign markets are exposed to this risk. Changes in exchange rates can affect the value of foreign currency-denominated assets and liabilities.
Identifying and Measuring Market Risk
Identifying and measuring market risk is crucial for developing effective risk management strategies. One widely used measure for this purpose is Value at Risk (VaR).
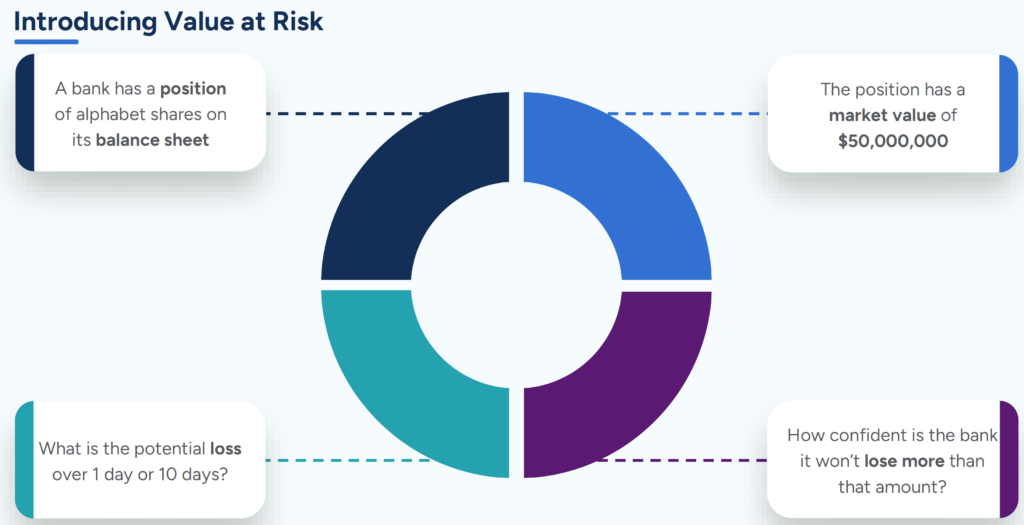
Value at Risk (VaR)
Value at Risk (VaR) is a statistical measure that estimates the potential loss in value of an asset or portfolio over a specified period, given normal market conditions. It provides a quantifiable measure of market risk and is widely utilized by financial institutions to assess their risk exposure.
The most common VaR method used by banks requires historical returns data and assumes that past market behavior is a good indicator of future market performance. By analyzing the historical price volatility and correlations among asset classes, VaR calculates the maximum expected loss within a certain confidence level (e.g., 95% or 99%) over a specified time horizon (e.g., one day or one month).
While VaR is a powerful tool, it has limitations. It does not account for extreme market events or “black swan” events, and it assumes normal market conditions, which may not always hold true. Therefore, it is essential to complement VaR with other risk management techniques.
Managing Market Risk
Effective market risk management involves a combination of strategies to mitigate potential losses and protect financial performance. Here are some key strategies for managing market risk:
Diversification
Diversification is the practice of spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographical regions to reduce risk. A diversified portfolio is less likely to experience significant losses due to the poor performance of a single investment. By holding a mix of stocks, bonds, commodities, and foreign currencies, investors can achieve a balance that minimizes market risk.
Hedging
Hedging involves using financial instruments, such as options, futures, and swaps, to offset potential losses from adverse market movements. For example, a company exposed to currency risk might use foreign exchange futures to lock in exchange rates and protect against unfavorable fluctuations. Hedging can effectively reduce market risk, but it also requires careful planning and execution.
Stress Testing and Scenario Analysis
Stress testing and scenario analysis involve evaluating the impact of hypothetical scenarios on an investment portfolio or financial institution. By simulating extreme market conditions, such as a sudden interest rate hike or a sharp decline in stock prices, financial professionals can assess the potential losses and identify vulnerabilities. This information is crucial for developing robust risk management strategies.
Liquidity Management
Liquidity management ensures that a financial institution or investment portfolio has sufficient liquid assets to meet short-term obligations and withstand market fluctuations. Maintaining a buffer of cash or highly liquid securities can provide a safety net during periods of market stress, reducing the need to sell assets at unfavorable prices.
Constant Monitoring and Rebalancing
Market conditions are dynamic, and risk exposure can change over time. Regularly monitoring the portfolio and rebalancing it to align with the desired risk tolerance is essential for effective risk management. Rebalancing involves adjusting the allocation of assets to maintain the desired level of risk and return.
Volatility Management
Volatility management focuses on strategies to mitigate the impact of price volatility on the portfolio. Techniques such as using low-volatility stocks, employing options strategies, and implementing stop-loss orders can help manage the adverse effects of market fluctuations.
Quantitative Analysis and Models
Quantitative analysis and models use mathematical and statistical techniques to assess and manage market risk. These models can incorporate various risk factors, such as interest rates, stock prices, and currency exchange rates, to provide insights into potential losses and risk exposures. While quantitative models are powerful tools, they require accurate data and ongoing validation.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is crucial for financial institutions to ensure they meet legal and regulatory requirements related to market risk management. Regulatory bodies often mandate specific risk management practices, reporting standards, and capital adequacy requirements. Adhering to these regulations not only ensures compliance but also enhances the institution’s risk management framework.
The Role of Risk Management Professionals
Risk management professionals play a crucial role in identifying, assessing, and mitigating market risk within their organizations. Understanding market risk fundamentals is essential for making informed financial decisions, optimizing investment strategies, and safeguarding the company’s financial health.

Responsibilities of Risk Management Professionals
Risk management professionals are responsible for overseeing the risk management framework of an organization. This includes identifying potential market risks, assessing their impact, and developing strategies to manage and mitigate these risks effectively.
Assessing Investment Opportunities
When evaluating investment opportunities, risk management professionals must consider the associated market risks. For instance, investing in fixed income securities requires an understanding of interest rate risk and its potential impact on the portfolio’s value. Similarly, investing in foreign markets necessitates an assessment of currency risk and its implications.
Developing Risk Management Strategies
Risk management professionals must develop and implement comprehensive risk management strategies to protect the organization’s assets and financial performance. This involves diversifying the investment portfolio, using hedging techniques, and conducting stress tests to identify vulnerabilities. By proactively managing market risk, risk management professionals can minimize potential losses and ensure financial stability.
Communicating Risk to Stakeholders
Effective communication of market risk to stakeholders, including senior management, investors, and regulatory authorities, is crucial. Risk management professionals need to provide clear and comprehensive risk assessments, highlighting potential exposures and the steps taken to mitigate them. Transparent communication builds trust and confidence among stakeholders.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The financial markets are constantly evolving, and market risk dynamics can change rapidly. Risk management professionals must stay updated with the latest market trends, regulatory changes, and risk management practices. Continuous learning and adaptation are essential for staying ahead in managing market risk effectively.
By fulfilling these roles and responsibilities, risk management professionals ensure that their organizations are better prepared to navigate the complexities of market risk and achieve long-term financial success. For those looking to deepen their understanding of market risk, CFI offers a comprehensive Market Risk Fundamentals course that provides valuable insights and practical knowledge.
Conclusion
Market risk is an inherent aspect of investing and financial management that can significantly impact financial institutions and corporate finance professionals. By understanding the various types of market risk, identifying and measuring it using tools like Value at Risk (VaR), and implementing effective risk management strategies, financial professionals can mitigate potential losses and safeguard their financial performance.
As the financial markets continue to evolve, staying informed and proactive in managing market risk is essential for achieving long-term financial success. By embracing best practices in risk management and continuously enhancing their knowledge and skills, financial professionals can confidently navigate the uncertainties of the market and achieve their financial goals.
Additional Resources
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide on Market Risk. To keep advancing your career and skills, the following CFI resources will be useful:

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in