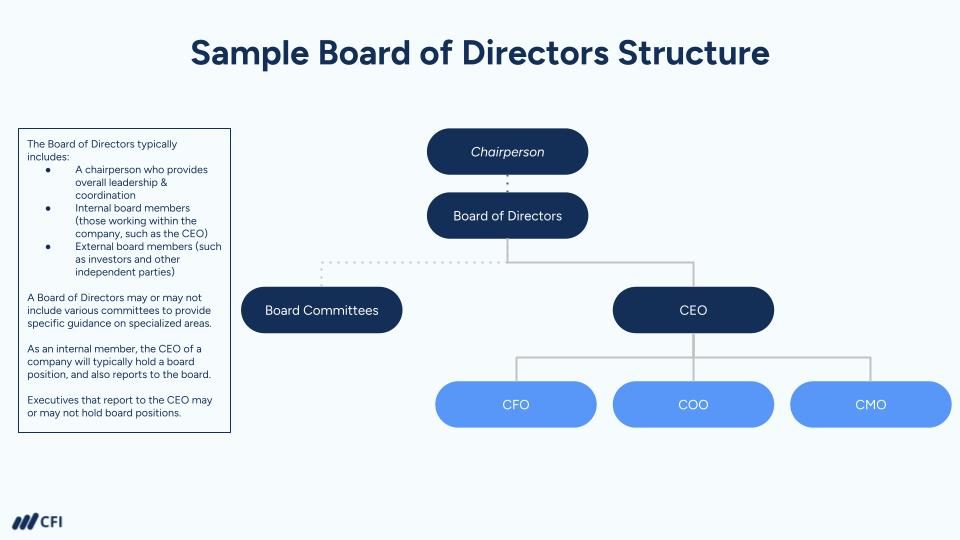
Board of Directors
A panel of individuals that are elected to represent shareholders
What is a Board of Directors?
A board of directors is a panel of people who are elected to represent shareholders. Every public company is legally required to have a board of directors. Nonprofits and many private companies, while not required to have a board of directors, may elect to have one to help govern and guide the organization.

A board of directors is responsible for protecting shareholders’ interests, establishing management policies, overseeing the governance of the corporation or organization, and making critical business decisions.
What Does a Board of Directors Do?
The board of directors is a group of individuals who are responsible for overseeing the management and direction of a company or organization. In a broad sense, a corporate board of directors acts as a fiduciary for shareholders. The board has several key roles and responsibilities, including:
- Hiring and overseeing senior management: The board hires the CEO and other senior executives and is responsible for overseeing their performance and ensuring that they are acting in the best interests of the company.
- Monitoring financial performance: The board reviews the company’s financial statements and ensures that the company is managing its finances responsibly.
- Ensuring compliance with legal and ethical standards: The board is responsible for ensuring that the company is complying with all applicable laws and regulations, as well as maintaining high ethical standards.
- Providing guidance and support to management: The board provides guidance and support to senior management as needed, and may offer advice on key business decisions or challenges.
- Representing the interests of shareholders: The board represents the interests of the company’s shareholders, and works to ensure that the company is maximizing shareholder value.
- Setting the overall direction and strategy of the company: The board is responsible for setting the company’s strategic goals and direction, and ensuring that management is taking the necessary steps to achieve those goals.
Overall, the board of directors plays a critical role in ensuring that the company is operating in a responsible and effective manner, and that it is delivering value to its shareholders and other stakeholders.
Common Structure of a Board of Directors
The structure, responsibilities, and powers given to a board of directors are determined by the bylaws of a company or organization. The bylaws determine how many board members there will be, how the members will be elected, and how frequently the board members will meet. While best practices exist, there’s no set structure for a board of directors. The composition and role of the board of directors will depend largely on the industry, stage, funding, and organizational needs.
The board’s role is to represent shareholder and owner/management interests and provide oversight of business operations and is typically composed of both internal and external members.
Internal members of a board of directors are typically individuals who are employed by the organization and have a direct stake in its success. These individuals may include executives, such as the CEO or CFO, or other senior leaders within the organization.
External members of a board of directors are individuals who are not employed by the company or organization. External members may include investors who have funded the company, or independent members.
Independent board members are often chosen for their expertise in a particular industry or field or for their experience in corporate governance.
Whether investors or independent, external board members can provide a valuable outside perspective and may bring skills and knowledge that are not present within the company. They also help ensure that the interests of shareholders and other stakeholders are represented and that the company is operating responsibly and ethically.
Although external board members may or may not have a financial stake in the company, they have a professional reputation to uphold and a responsibility to act in the company’s and its stakeholders’ best interests. In many cases, external board members are compensated for their service on the board, which provides additional incentive to act in the company’s best interests.
Both internal and external members of a board of directors have an important role to play in overseeing the management of a company or organization and ensuring its long-term success.
As the most senior executive within a company, the CEO typically is a member of the board of directors and also reports to the board of directors.
International structure of a board of directors
The structuring of a board of directors tends to be more varied outside of the United States. In certain countries in Asia and the European Union, the structure is often split into two primary boards — executive and supervisory.
The executive board is made up of company insiders that are elected by employees and shareholders. In most cases, the executive board is headed up by the company CEO or a managing officer. The board is typically tasked with overseeing the daily business operations.
The supervisory board concerns itself with a broader spectrum of issues when dealing with the company and acts much like a typical U.S. board. The chair for the board varies but is always headed up by someone other than the preeminent executive officer.
Role of the chairperson
The role of the chairperson of a board of directors is to provide leadership and guidance to the board in fulfilling its responsibilities. The chairperson is typically responsible for setting the agenda for board meetings, facilitating discussions, and representing the board to outside stakeholders. Some of the specific duties of the chairperson may include:
- Leading board meetings: The chairperson presides over board meetings, sets the agenda, and ensures that all board members participate in discussions.
- Facilitating communication among board members: The chairperson may be responsible for ensuring that board members are kept informed about important developments within the company and that they have the information they need to make informed decisions.
- Representing the board to outside stakeholders: The chairperson may serve as the primary spokesperson for the board and may communicate with shareholders, customers, and other stakeholders on behalf of the board.
- Working closely with the CEO: The chairperson typically works closely with the CEO to ensure that the company is being managed effectively and that the board is providing appropriate oversight.
- Ensuring that the board is fulfilling its responsibilities: The chairperson is responsible for ensuring that the board is fulfilling its responsibilities, including setting the strategic direction of the company, overseeing management, and ensuring compliance with legal and ethical standards.
- Promoting good governance practices: The chairperson may work to promote good governance practices within the organization and ensure that the board is adhering to best practices for corporate governance.
In summary, the role of the chairperson of a board of directors is to provide leadership and guidance to the board in fulfilling its responsibilities and to represent the board to outside stakeholders.
Role of board committees
Board committees are smaller groups of board members that are created to focus on specific issues or areas of responsibility. The exact structure and function of board committees may vary depending on the organization, but some of the most common types of committees include:
- Audit Committee: This committee is responsible for overseeing the company’s financial reporting and internal control processes. They work closely with the company’s external auditors to review the financial statements, ensure compliance with accounting standards, and identify any potential areas of risk.
- Compensation Committee: This committee is responsible for setting and reviewing the compensation packages for senior executives and board members. They ensure that the company’s compensation practices are aligned with its strategic goals and are competitive within the industry.
- Nominating and Governance Committee: This committee is responsible for identifying and evaluating potential candidates for board membership, as well as overseeing the governance practices of the company. They ensure that the board is composed of individuals with the necessary skills and expertise to guide the company’s strategic direction.
- Risk Management Committee: This committee is responsible for identifying and managing potential risks to the company, including operational, financial, and strategic risks. They develop risk management strategies and ensure that the company has appropriate policies and procedures in place to mitigate potential risks.
- Corporate Social Responsibility Committee: This committee is responsible for overseeing the company’s efforts to promote social responsibility and environmental sustainability. They ensure that the company is adhering to best practices for corporate social responsibility and is taking a leadership role in addressing social and environmental issues.
Overall, the role of board committees is to provide focused oversight and expertise on specific areas of responsibility and to make recommendations to the full board of directors on important issues. Not every board of directors have committees.
Additional Resources

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in