Data Sources in Financial Modeling
Find relevant data for financial modeling
Data Sources in Financial Modeling
Collecting and using the right data sources in financial modeling is crucial to the success of financial analysis. Financial modeling requires gathering and analyzing lots of information; the collection of data is a crucial step in creating a financial model. There is a wide range of data that must be used in a financial model. A company’s historical results are the key input to prepare a three-statement model, which is the setup for all other financial models.

Management discussion and analysis from corporate filings, industry reports, and research reports of professional analysts are some of the resources that may improve the accuracy of your forecasting assumptions. Finally, you need to find the appropriate inputs for your valuation. Knowledge of relevant data sources is critical for an analyst to develop a precise and up-to-date model.
Data Sources: Company Reports and Regulatory Filings
Governments place special attention on public companies. There are mandatory reporting standards for public companies that are regulated by government entities.
Due to its nature, a public company bears a responsibility to its shareholders. Governments regulate the actions of public companies through mandatory reporting requirements and standards. In accord with existing legislation, public companies must disclose all material information about their operations and performance.
Companies must prepare an annual report to the shareholders, in which corporate information is disclosed. These reports include financial data, results of operations, market segment information, new product plans, subsidiary activities, and research and development activities. The annual reports to shareholders are usually posted on the company’s website.
In the United States, the primary regulatory entity is the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Public companies must submit their filings to the SEC regularly. SEC filings are comprehensive documents that include fundamental information about the company and its operations. For the purpose of financial modeling, the most relevant filings for an analyst are:
| Filing | Description |
|---|---|
| Registration Statements | A description of the company’s properties and business; a description of the security to be offered for sale; information about the management of the company; financial statements certified by independent accountants |
| 10-K | Annual report outlining a comprehensive overview of the company’s business and financial condition. 10-K includes audited financial statements. |
| 10-Q | Quarterly report with a continuing view of the company’s financial position during the year. 10-Q includes unaudited financial statements. |
| 8-K | Report of current events to announce major events that shareholders should know about. |
| Schedule 13-D | Reports acquisition of beneficial ownership of more than 5% of a voting class of a company’s equity securities by a person or a group of persons. |
| Proxy Statements | Statements filed by companies prior to shareholders meetings to provide shareholders with information necessary to make informed decisions. |
| Form 3 | Filed by the corporate insiders (company’s officers and directors) who are registering equity securities for the first time. |
| Form 4 | Filed after a material change in the holdings of company insiders. |
| Form 5 | Filed by an insider who conducted insider transactions during the year that were not previously reported in a Form 4. |
All the submitted filings may be retrieved from the EDGAR database maintained by the SEC.
In Canada, public companies follow a similar process to that of US-based public companies. Even though the Canadian system of securities regulation is not unified, and each province has its own regulatory entity, a single database (SEDAR) contains all the forms filed by the publicly traded companies across the country. The U.S. and Canadian filings comparison is provided in the table below:
| U.S. Filings | Canadian Filings |
|---|---|
| 10-K | Annual Report, Annual Information Form, Management Proxy Circular |
| 10-Q | Interim Financial Statement |
| 8-K | Material Change Report |
In the U.K., all publicly traded companies (Public Limited Companies or PLCs) must submit required filings to Companies House, which is a registrar of the companies. On the Companies House website, you can find the database of the filings submitted by companies registered in the U.K. The companies submit annual reports, statements of annual return, and announcements of major events.
In Japan, one of the largest financial markets in Asia, the regulation of public companies is very strict. Every public company must comply with the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act and submit its financial statements, internal control reports, and quarterly reports, audited by CPAs, to the Financial Services Agency (FSA).
The FSA is a Japanese government agency and regulator of the country’s financial system. Companies provide the necessary filings to FSA online through the EDINET system. This system is available online to the public.
Data Sources: Financial Databases
Companies such as Bloomberg, Capital IQ, and Thompson Reuters provide powerful databases of financial data. These databases provide access to various types of financial information, including historical financials from financial statements. Financial databases allow you to analyze the historical data and easily export the data into Excel.
However, financial statements retrieved from these databases tend to be in a standardized format. Thus, if the company uses an accounting system unique to its business operations, you will not grasp it from data retrieved, affecting your analysis.
Nevertheless, financial databases are great sources of various types of data that can be helpful in financial modeling. Key economic factors, M&A transactions, comparables analysis, analysis of securities – including equities, bonds, and derivatives, and analysts’ reports – are some of the many useful tools that may be used in financial modeling.
Related Information
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Data Sources in Financial Modeling. To continue learning and developing your skills, these additional free CFI resources will be helpful:
Analyst Certification FMVA® Program
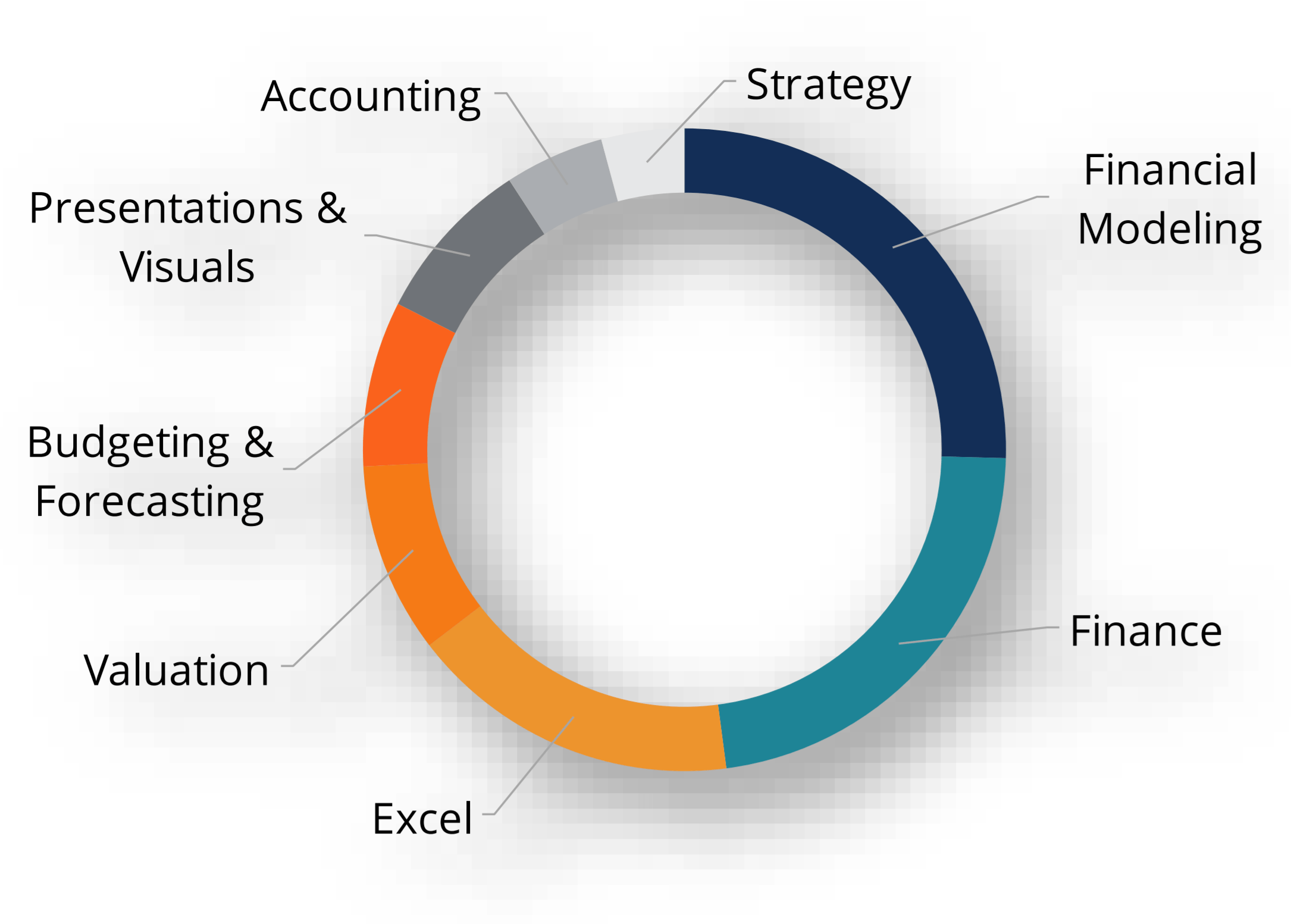
Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy.
A well rounded financial analyst possesses all of the above skills!
Additional Questions & Answers
CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation. CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path. In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path.
In order to become a great financial analyst, here are some more questions and answers for you to discover:
- What is Financial Modeling?
- How Do You Build a DCF Model?
- What is Sensitivity Analysis?
- How Do You Value a Business?
Additional Resources
CFI is a global provider of financial modeling courses and of the FMVA Certification. CFI’s mission is to help all professionals improve their technical skills. If you are a student or looking for a career change, the CFI website has many free resources to help you jumpstart your Career in Finance. If you are seeking to improve your technical skills, check out some of our most popular courses. Below are some additional resources for you to further explore:
The Financial Modeling Certification
Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in